Statement
A body moves between any two instants of time following a circular path with a radius of 5 meter, as you can see in the figure.
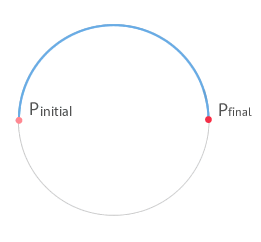
Determine:
- The displacement vector of the body and the distance traveled, assuming the origin of the system of reference is located at the starting point of the motion
- The displacement vector of the body and the distance traveled, assuming the origin of the system of reference is in the center of the semicircle
Solution
1. We are in a similar situation to the following figure:
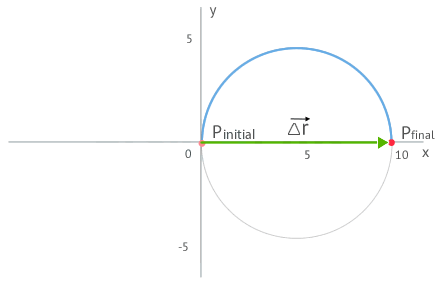
The displacement vector corresponds to the vector connecting the starting point to the final point. Analyzing the drawing, we can see that the magnitude of the displacement vector is equal to the diameter of the semicircle, the direction will be the same as the direction of the positive x axis.
We could have calculated it analytically, starting with the expression of the displacement vector
As to the distance traveled, since the trajectory of the movement is a semicircle, its value coincides with the length of the semicircle:
2. We are in a similar situation to the following figure:
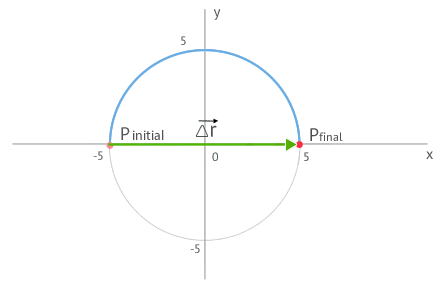
The displacement vector corresponds to the vector connecting the starting point with the final point. In this case
As you can see, the displacement vector has the same value as in 1, despite having placed the origin of the reference system at a different location. Therefore, the displacement of the body is independent of where you place the origin.
Regarding the distance travel, those calculations are the same that in the previous paragraph.

